AVERAGEA Function. Get the average including non-numeric values.
Get the average including non-numeric values.
How it works
=AVERAGEA(number1 to 255)
| Name | Omission | Specify |
|---|---|---|
| number1 to 255 | Required argument. | The number to be averaged. |
Example Results
Specify cell range.
Basically, a range of cells is specified.
Non-numeric characters are mixed in
If non-numeric characters such as alphabetic characters are mixed in, the non-numeric characters are averaged as 0.
In this example, there is a difference between the AVERAGE function and this.
| Function | Calculation. |
|---|---|
| AVERAGE | Ignore "A". Result is 2.5. |
| AVERAGEA | Calculate "A" as 0. Result is 2. |
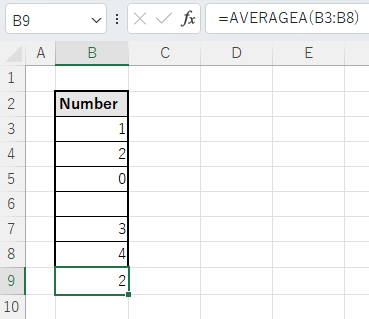
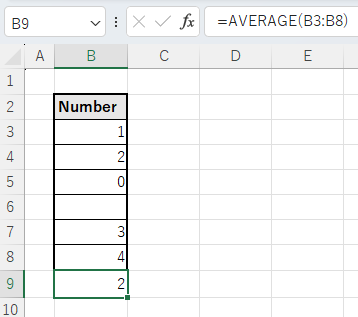
0 and blank
Zeros are included in the average calculation, but spaces are ignored.
In the example below, the calculation is 10 divided by 5.
This rule is identical to the AVERAGE function.
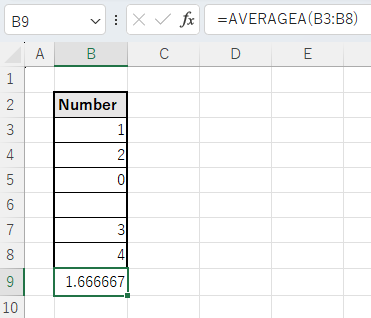
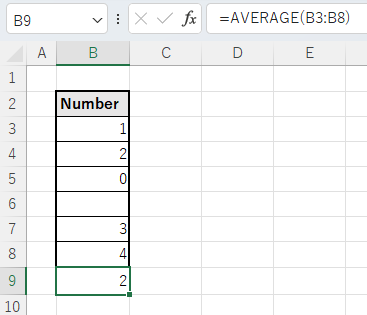
However, if a cell contains a formula such as ="", it will be treated as 0 even though it looks the same as a blank space.
This behavior differs from that of the AVERAGE function.
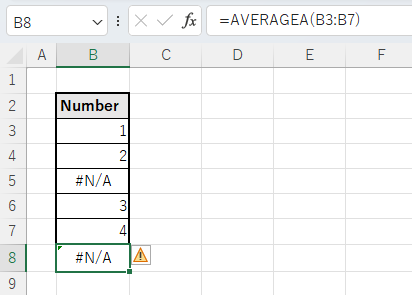
Error value
If an error cell is mixed in, the AVERAGE function will also result in an error.
This should be noted when including the results of XLOOKUP and VLOOKUP functions in the calculation.
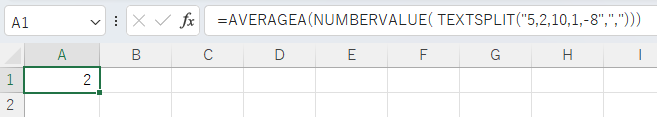
Specify other than cell range.
It is also possible to return a range of cells as the result of a function argument. In this case, the average value is taken from the result of the function.
List of functions that result in a range of cells.
| Function | Category | Description |
|---|---|---|
| TEXTSPLIT | Text | Divides text into cells based on a specified character. |
| XLOOKUP | Lookup & Reference | Get data matching the search value. |
| FILTER | Lookup & Reference | Get a list of data that matches the condition. |
| UNIQUE | Lookup & Reference | Delete duplicate data in a specified cell range. |
| SEQUENCE | Lookup & Reference | Create sequential numbers in multiple cells. |
| SORT | Lookup & Reference | Sort a range of cells by a specified column. |
| SORTBY | Lookup & Reference | Sort a cell range by specifying multiple reference columns. |
| DROP | Lookup & Reference | elete a specified number of rows and columns from a specified cell range. |
| TAKE | Lookup & Reference | Obtains a specified number of rows and columns from a specified cell range. |
| TOCOL | Lookup & Reference | Arranges a specified range of cells in a single column. |
| TOROW | Lookup & Reference | Sort a specified range of cells into a single column. |
| EXPAND | Lookup & Reference | Extended specified cell range. |
| CHOOSEROWS | Lookup & Reference | Get the row at the specified position from the specified cell range. |
| CHOOSECOLS | Lookup & Reference | Get the column at the specified position from the specified cell range. |
| WRAPROWS | Lookup & Reference | Sort a range of cells in a single column or row by a specified number of rows. |
| WRAPCOLS | Lookup & Reference | Sort a range of cells in a column or row by a specified number of columns. |
| VSTACK | Lookup & Reference | Merge multiple cell ranges in row direction. |
| HSTACK | Lookup & Reference | Merge multiple cell ranges in column direction. |
| TRANSPOSE | Lookup & Reference | Create a cell range with the rows and columns of the specified cell range swapped. |
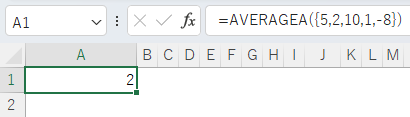
It can also be specified as an array.
=AVERAGEA({5,2,10,1,-8})
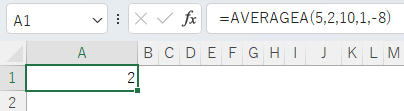
Multiple values can also be specified simply by separating them with commas.
=AVERAGEA(5,2,10,1,-8)
Multiple cells can be specified by separating them with commas.
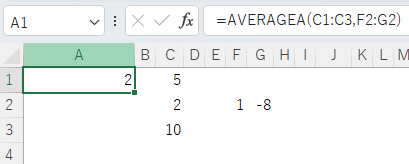
Spill
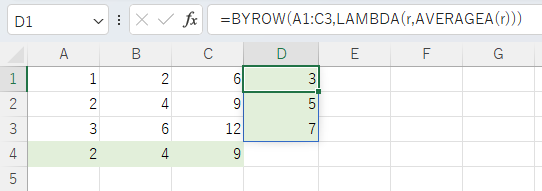
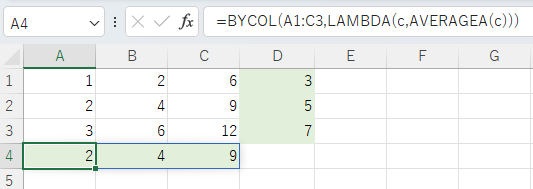
Spill when using the BYROW or BYCOL function.
=BYROW(A1:C3,LAMBDA(r,AVERAGEA(r)))
=BYCOL(A1:C3,LAMBDA(c,AVERAGEA(c)))
---
Discussion
New Comments
No comments yet. Be the first one!