DCOUNT function. Get the number of numerical counts by specifying the aggregate items and search conditions.(Microsoft Excel)
This function retrieves the number of numerical counts by specifying items and conditions.
If you want to include non-numeric items, use the DCOUNA function.
What is a database in Excel functions?
A database is a table with item names in the first row and rows of data underneath.
It is a database in the Excel functions.
How it works
=DCOUNT(Database,Field,Criteria)
| Argument | Omission | Specify |
|---|---|---|
| Database | Required argument. | Determination target. Specify the range of the table containing the item name. In the aforementioned sample, A2 to C13. |
| Field | Required argument. | Field to be calculated. |
| Criteria | Required argument. | Conditions to be calculated. |
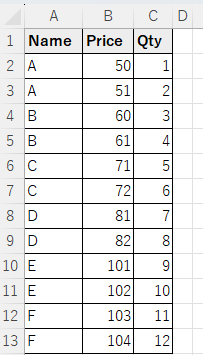
Example Results
One condition. Use column name for Field
Target cell range in argument 1.
"Price" and "Qty" in argument 2.
"Name" is "C" as the condition.
The number of "Price" is displayed in E5 and the number of "Qty" in E6.
Zero counts as one case, but blanks do not.
Therefore, "Price" counts as 2 and "Qty" counts as 1.
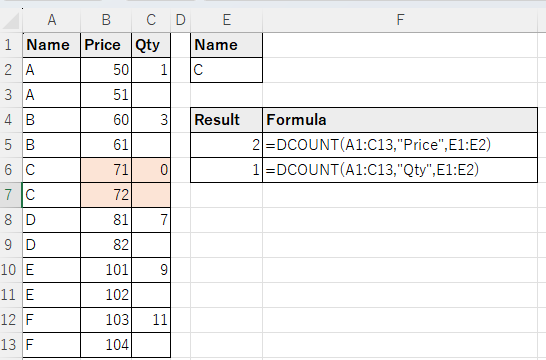
One condition.Use column number for Field
Items can be numbered consecutively with the leftmost number being 1.
In most cases, item names are recommended because they make the formulas more readable.
However, if the item names change frequently, column numbers are better.
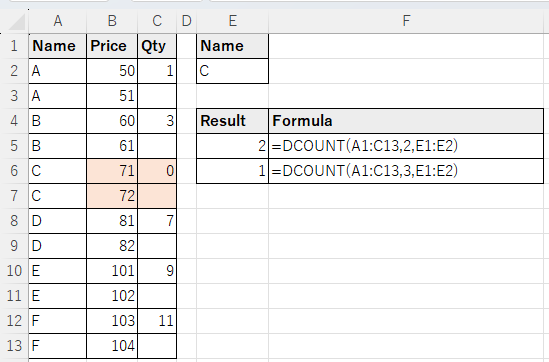
Multiple condition specification (logical OR).
Arranging the conditions vertically results in a logical sum.
In cell E6 of the example below, the rows corresponding to "C" and "D" are counted.
Multiple condition specification (logical AND).
When the conditions are arranged horizontally, they become "AND" condition specifications.
In the example below, the rows that correspond to any of "B," "C," "D," and "E" (Blue background) and also correspond to "Price" of 82 or more (Green background) are counted. (Red background color is the target of calculation)
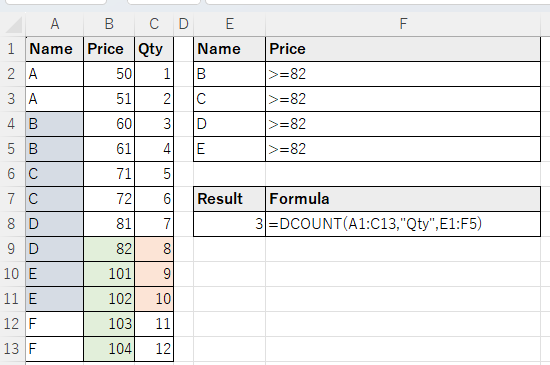
Multiple condition specification. (Range of values)
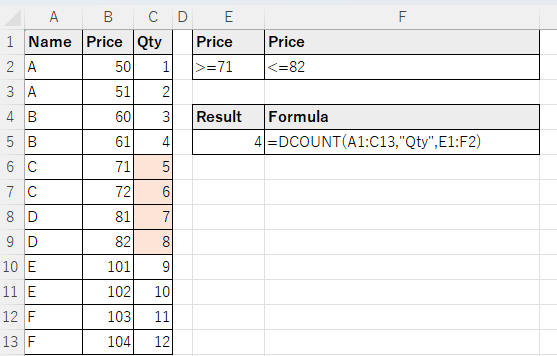
A range of conditions can also be specified, such as "greater than or equal to" or "less than or greater than.
To do so, specify a comparison operator with the same items side by side.
---
Discussion
New Comments
No comments yet. Be the first one!