Associative array.(Microsoft Excel Office Scripts)
Introduction to the use of associative arrays in Office scripts.
Operations
Associative arrays are managed with "tesx (type string)" or "non-sequential integer (type number)" keys instead of integer sequential numbers (indexes),
An associative array manages arrays with keys that are either strings or non-sequential integers (type number).
Associative arrays are also called hashes or dictionaries.
Create associative array
This associative array is declared as follows.
let variable name: { [key: key data type]: item data type } = {};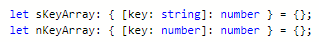
Initialize Set the item as soon as it is created
To initialize the contents, separate the keys and values with a : and separate the items with a ,.
Duplicate values are allowed within the same associative array, but duplicate keys are prohibited.
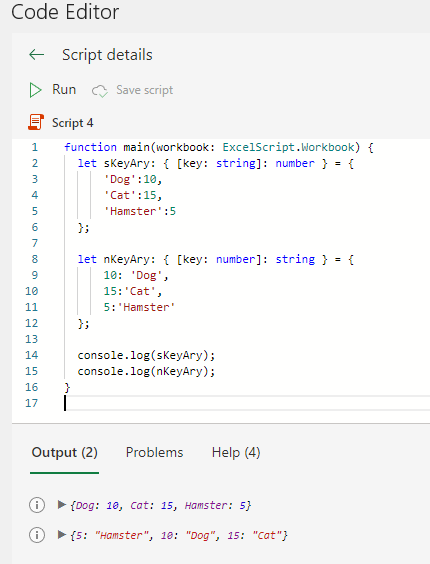
let variable name: { [key: key data type]: item data type } = { key:value,key:value… };function main(workbook: ExcelScript.Workbook) {
let sKeyAry: { [key: string]: number } = {
'Dog':10,
'Cat':15,
'Hamster':5
};
let nKeyAry: { [key: number]: string } = {
10: 'Dog',
15:'Cat',
5:'Hamster'
};
console.log(sKeyAry);
console.log(nKeyAry);
}
Retrieve items
Specified key item
associative array variable[key]; //
Bracket notation
associative array variable.key; // Property notationThere are two notation methods, but the bracket notation is recommended.
The property notation cannot be used if the key is a number or if the first letter is a number.
The bracketed notation is more easily recognized as an array.
Key check
In the case of associative arrays, if you specify a key that does not exist, it will work without error.
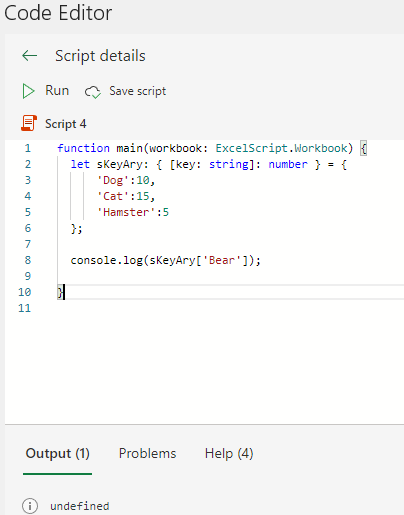
To determine if a key exists, do the following
key in associative array variableTrue if the specified key exists in the associative array,false if the specified key does not exist.
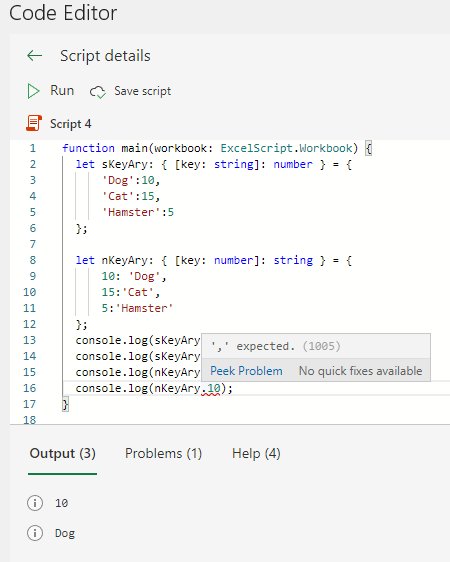
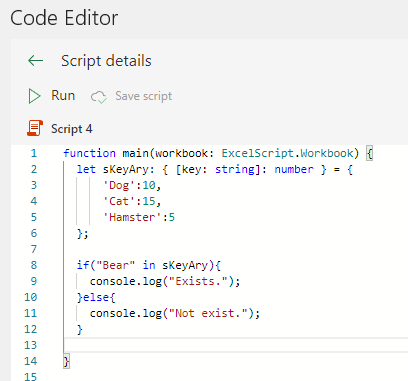
function main(workbook: ExcelScript.Workbook) {
let sKeyAry: { [key: string]: number } = {
'Dog':10,
'Cat':15,
'Hamster':5
};
if("Bear" in sKeyAry){
console.log("Exists.");
}else{
console.log("Not exist.");
}
}
All keys (loop)
for (let key variable
of associative array variable){
key variable; // Current key
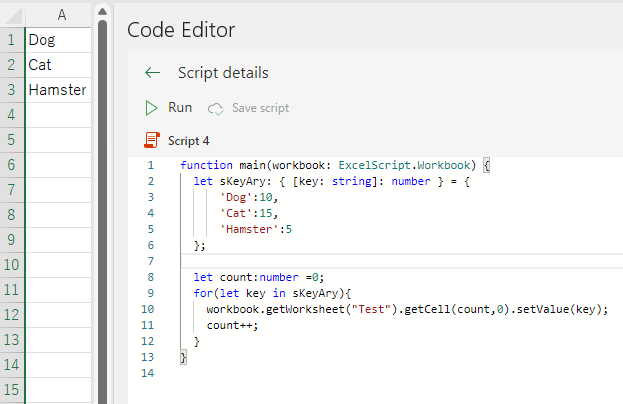
}function main(workbook: ExcelScript.Workbook) {
let sKeyAry: { [key: string]: number } = {
'Dog':10,
'Cat':15,
'Hamster':5
};
let count:number =0;
for(let key in sKeyAry){
workbook.getWorksheet("Test").getCell(count,0).setValue(key);
count++;
}
}
All keys (array)
Object.keys(associative array variable);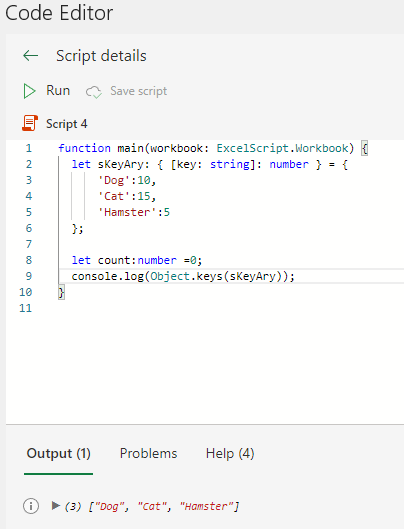
All items (loop)
for (let
key variable
of associative array variable){
associative array variablekey variable]; // Value of the current item
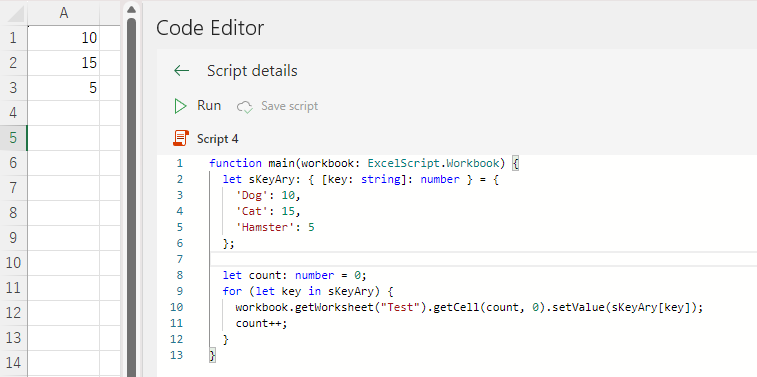
}function main(workbook: ExcelScript.Workbook) {
let sKeyAry: { [key: string]: number } = {
'Dog': 10,
'Cat': 15,
'Hamster': 5
};
let count: number = 0;
for (let key in sKeyAry) {
workbook.getWorksheet("Test").getCell(count, 0).setValue(sKeyAry[key]);
count++;
}
}
Add or Change items
associative array variable[key] = value;If the specified key exists, it is changed; if not, it is added.
Number of items
Because the length method cannot be used as it is,keys and use the length method.
Object.keys(associative array variable).length;Delete items
Specified key
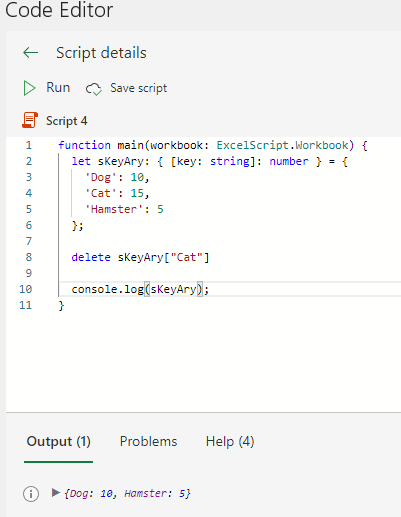
delete associative array variable[key]function main(workbook: ExcelScript.Workbook) {
let sKeyAry: { [key: string]: number } = {
'Dog': 10,
'Cat': 15,
'Hamster': 5
};
delete sKeyAry["Cat"]
console.log(sKeyAry);
}
All items
associative array variable = {};Merge
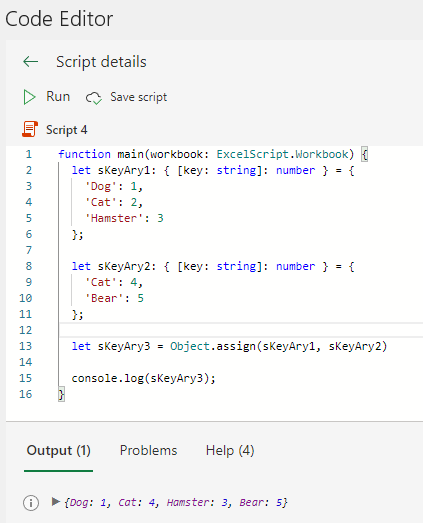
If there are duplicate keys, the value will be the value of the associative array specified after it.
ater merge variable = Object.assign(variable1, variable2)function main(workbook: ExcelScript.Workbook) {
let sKeyAry1: { [key: string]: number } = {
'Dog': 1,
'Cat': 2,
'Hamster': 3
};
let sKeyAry2: { [key: string]: number } = {
'Cat': 4,
'Bear': 5
};
let sKeyAry3 = Object.assign(sKeyAry1, sKeyAry2)
console.log(sKeyAry3);
}
Retrieve key from value
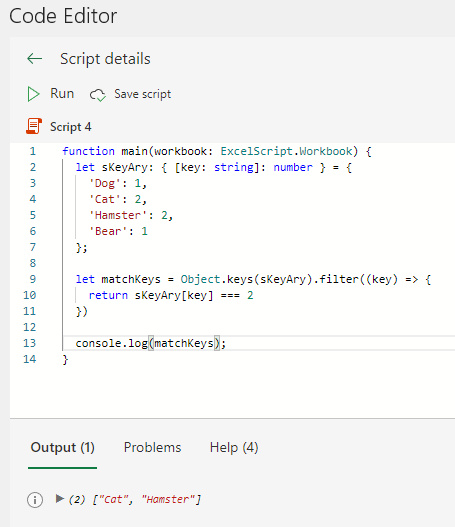
key array variable = Object.keys(associative array variable).filter((key) => {
return associative array variable[key] === value
})In the following example, "2" is searched and the matching "Cat" and "Hamster" are retrieved as an array.
function main(workbook: ExcelScript.Workbook) {
let sKeyAry: { [key: string]: number } = {
'Dog': 1,
'Cat': 2,
'Hamster': 2,
'Bear': 1
};
let matchKeys = Object.keys(sKeyAry).filter((key) => {
return sKeyAry[key] === 2
})
console.log(matchKeys);
}
For those who want to learn Office script effectively
The information on this site is now available in an easy-to-read e-book format.
Or Kindle Unlimited (unlimited reading).

You willl discover how to about basic operations.
By the end of this book, you will be equipped with the knowledge you need to use Excel Office Script to streamline your workflow.
Discussion
New Comments
No comments yet. Be the first one!